BLOG
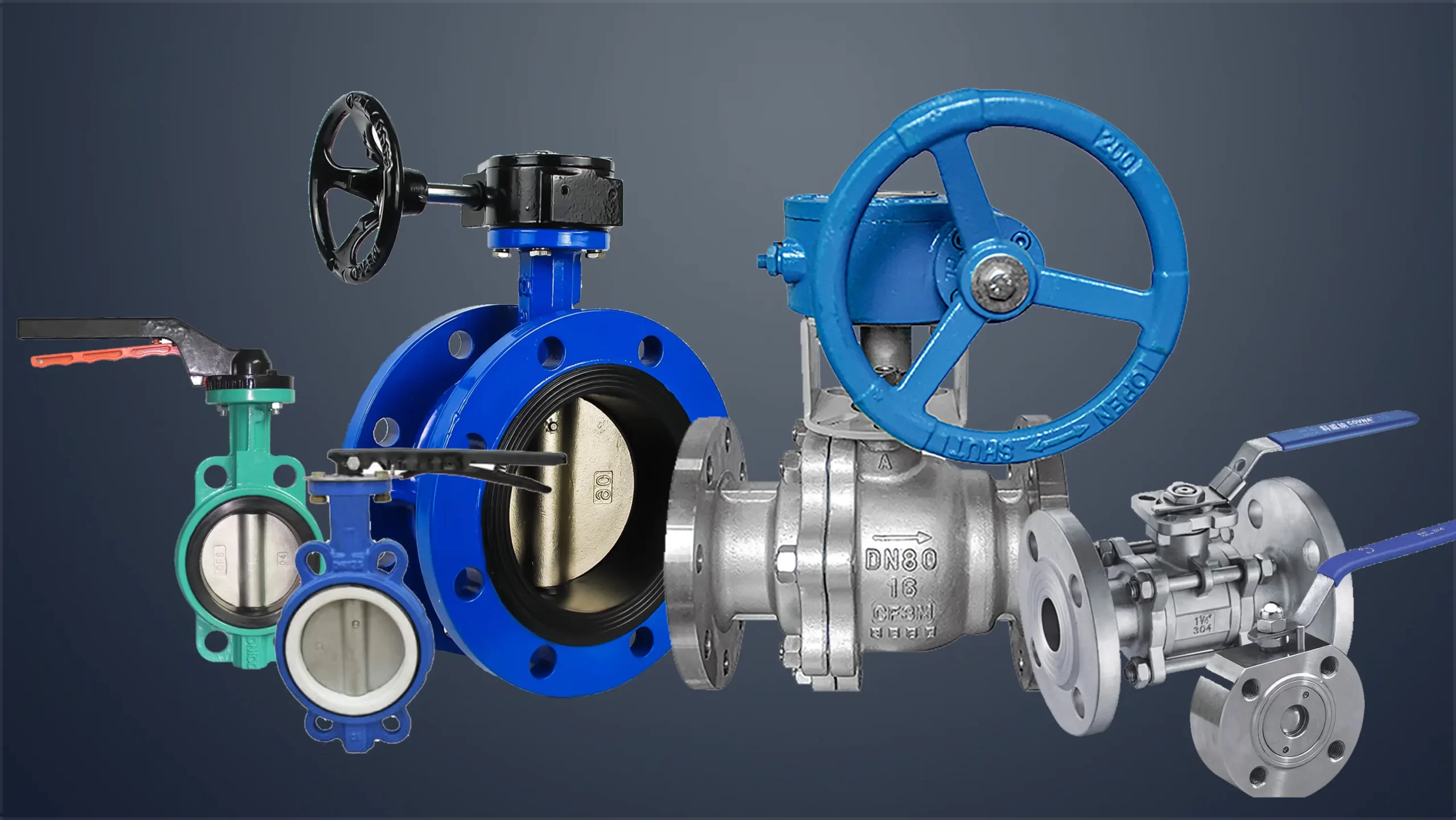
How many do the valves have?-by their connection type with pipeline
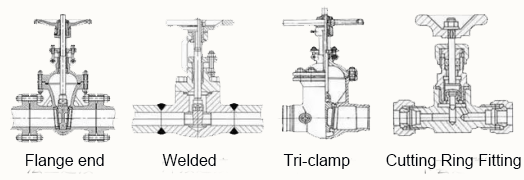
- Flange end connected valve: the valve body is equipped with flange, and the valve connected with the pipeline by flange;
- Threaded connection valve: valve body with screw thread, and pipeline with thread connection;
- Welding connection valve: valve body with welding port, and the valve connected with the pipeline by welding;
- Valve connected by clamp: valve with clamp mouth on the valve body and connected with pipeline by clamp;
- Valve connected by cutting ring fitting: valve connected by ferrule and pipeline.
As shown below:
Basic parameters of valve:
- Nominal diameter: the nominal diameter refers to the nominal diameter of the channel where the valve is connected with the pipeline, i.e. the round diameter used as a reference, expressed as DN. It indicates the size of the valve specification.
- Nominal pressure: the nominal pressure refers to the design given pressure related to the mechanical strength of the valve, expressed in PN. Refer to GB / t1048-2005 definition and selection of pipeline components PN (Engineering pressure) for nominal pressure series.
- British and American standards have been listed in the concept of Engineering pressure, but still use the class. There is no strict correspondence between the nominal pressure and the temperature reference of the scale. In the actual application process, the corresponding relationship between the two references is shown in the following table:
| Class | 150 | 300 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 900 | 1500 | 2500 |
| PN(MPa) | 2.0 | 5.0 | 6.3 | 10.0 | 14.0 | 15.0 | 25.0 | 42.0 |
Applicable medium:
according to the requirements of valve material and structure, the applicable medium of the valve is as follows:
- Gas medium, such as air, steam, nitrogen and natural gas, etc;
- Liquid media, such as oil, water, etc;
- Containing solid medium;
- Corrosive and highly toxic media.
More interesting video, pls visit our youtube!
Tags: COVNA valves
--- END ---